The Photon and Neutron Open Science Cloud (PaNOSC)
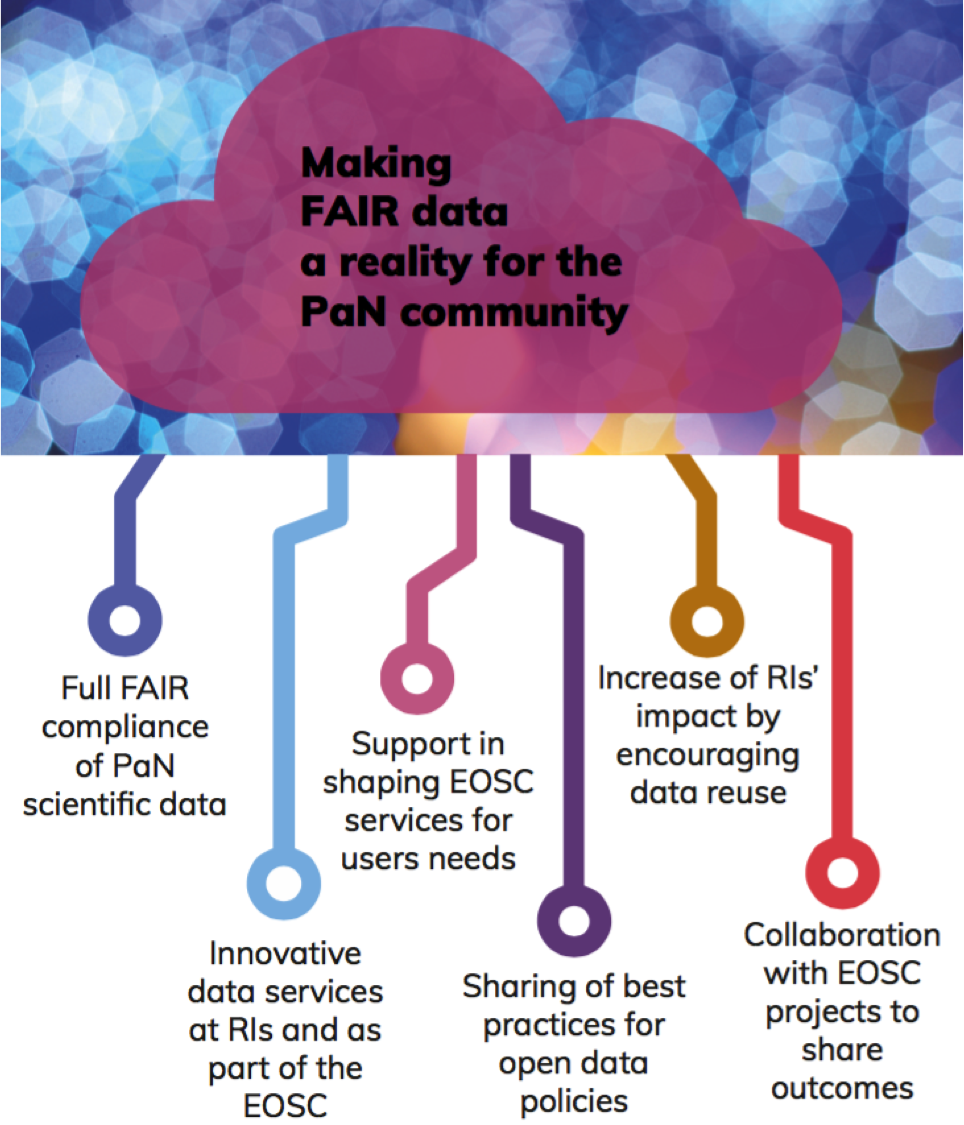
The Photon and Neutron Open Science Cloud (PaNOSC) is the science cluster representing Photon and Neutron European Research Infrastructures (RIs), developing and providing services for its scientific community and connecting these to the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC).
Objectives
- Participate in the construction of the EOSC by linking with the e-infrastructures and other science clusters.
- Make scientific data produced at Europe’s major Photon and Neutron sources fully compatible with the FAIR principles.
- Generalise the adoption of open data policies, standard metadata and data stewardship from all photon and neutron RIs and physics institutes across Europe
- Provide innovative data services to the users of these facilities locally and the scientific community at large via the EOSC.
- Increase the impact of RIs by ensuring data from user experiments can be used beyond the initial scope.
- Share the outcomes with the community at large to promote the adoption of FAIR data principles, data stewardship and the EOSC.
Mailing List
If you would like to be kept informed about the science cluster, its activities and results, please subscribe to our mailing list by clicking below:
Latest News
-
Published 15th March 2024

OSCARS launches its 1st Open Call for Open Science projects and services
On March 15th, the Science Clusters launched the first OSCARS cascading-grant call for Open Science projects and services. Over 300 attendees across and beyond Europe joined the online launch event and had the opportunity to interact with the panelists via an open Q&A session. As stated by OSCARS’ project coordinator, Giovanni Lamanna, “the aim of the […]
Read -
Published 4th March 2024

Science Clusters Position statement on operational commitment to EOSC and Open Research
The ESFRI Science Clusters, operating as a cluster of clusters in projects like OSCARS and EVERSE, have released the Science Clusters Position Statement on operational commitment to EOSC and Open Research, which articulates the Science Clusters’ vision for the future towards the successful implementation of the EOSC, as the result of five years of collaborative efforts, […]
Read -
Published 14th December 2023

OSCARS project funded to foster the uptake of Open Science in Europe
A wide range of publicly-funded Research Infrastructures (RIs) in Europe are organised in five major Science Clusters, which in the past four years implemented funded projects under the Horizon 2020 programme[1] to achieve a greater FAIRness of science[2], contributing to making research data FAIR: Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reproducible. These “Science Clusters” have strived to […]
Read
Use Cases
-
Published 5th July 2023
Use Case 32 - Reflectometry case study
Description of research Dr McCluskey et al. were interested in the structure of phospholipid monolayers at the surface of a novel Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES). They were able to collect a series of X-ray reflectometry data. However the analysis could not rely on the usual assumptions made about these materials previously measured on water. Challenge […]
Read -
Published 5th July 2022
Use case 31 - Seamless connection of Jupyter notebooks and GUI applications for e-learning purposes
Open education through MOOCs (massive open online courses) has attracted considerable attention in recent years, both due to availability in technology, and to a recent increase in demand for online content. The PaN e-learning platform is a portal which represents the joint effort of the PaN community. The PaNOSC and ExPaNDS projects have been building […]
Read -
Published 26th April 2022

Use Case 30 - VISA - Data Analysis in the Cloud
With the introduction of VISA (Virtual Infrastructure for Scientific Analysis) in June 2020, there has been a significant change with how scientists analyse experimental data and perform experiments at the ILL. Using a web browser, within a couple of minutes, a researcher can get access to a high-performance and secure data analysis environment, installed with […]
Read